Stringing in 3D Printing: What Is It and How Do You Fix It?
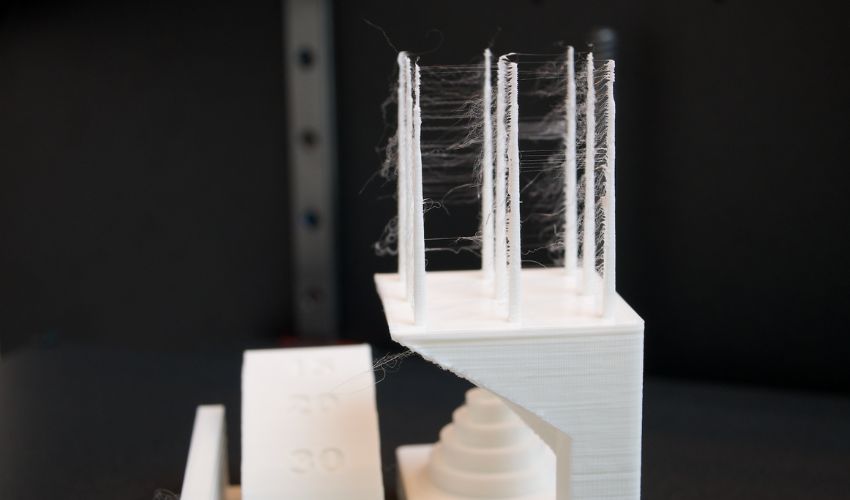
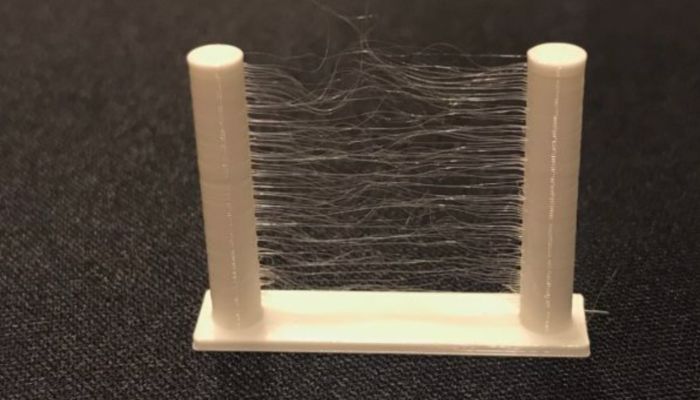
Relating to 3D printing, as with every manufacturing course of, it goes with out saying that customers is not going to at all times be fully happy with the outcomes. It may possibly typically occur that, as a result of completely different circumstances, the 3D printed half doesn’t fairly meet expectations and should due to this fact not be usable. One in every of these issues is what is called stringing in 3D printing. Because the identify already suggests, stringing leads to extraordinarily skinny, unintentional plastic threads on the half, paying homage to a spider’s internet. These unpleasant strings are a typical 3D printing problem. Furthermore, at the moment there are not any machine purposes that can be utilized to take away these threads, so this should be finished by hand or alternatively with warmth. Add on to that the truth that these threads can happen in massive portions, relying on the half, it’s secure to say that the elimination course of will be fairly sophisticated. We’ve got seemed extra carefully at stringing throughout 3D printing and clarify the way it happens and what you are able to do about it.
Using 3D printers thrives on nearly day by day improvements, so it’s typically unavoidable that challenges also can come up in reference to this. Stringing principally happens when utilizing filaments, basically the strings are tremendous, melted filament threads that settle in locations apart from they’re speculated to be on the 3D printed object. This could normally occur as a result of incorrect settings, in order that the filament continues to drip out of the nozzle regardless that the extruder is about to maneuver to a different location to proceed FDM 3D printing.
Photograph Credit: Elliot Saldukaite/3Dnatives
Right here’s how one can visualize the method: In case you’ve ever used a scorching glue gun, you’ve in all probability observed that even after you cease squeezing the new glue gun, it nonetheless creates extra melted glue. It is because there may be an excessive amount of strain contained in the gun. We are able to additionally apply this to the impact of stringing in 3D printing: a filament with a dimension of 1.75 mm, for instance, and a nozzle with a dimension of 0.4 mm – right here, too, there may be strain that causes the filament to circulation additional out of the nozzle leading to these threads. Theoretically, in fact, this shouldn’t occur, however there are some things you may remember to make sure that the melted filament is actually solely utilized to these components of the print the place you actually need them to be.
What Can You Do About Stringing in 3D Printing?
To keep away from having to cope with stringing when 3D printing, there are some things you may alter earlier than printing to in the end keep away from these pesky strings. Beginning with in all probability the obvious level: temperature. We all know that the extra filaments are heated, the extra fluid they’re. And the extra liquid they’re, the extra seemingly they’re to drip out of the nozzle throughout printing. Now, on the flip facet, if the temperature is simply too low, it could possibly’t soften the filament sufficiently, which limits the general 3D printing course of. So you need to discover the proper center floor that takes into consideration each the temperatures really helpful by the producer and the opposite print settings. Generally, the next temperatures apply to essentially the most generally used filaments: PLA – 180-210 °C; ABS – 210-250 °C; PETG – 210-230 °C; PVA – 160-190 °C and TPU – 220-240 °C. Nonetheless, it’s also really helpful to observe the general stringing scenario throughout 3D printing and act accordingly, decreasing the temperature in small increments when stringing happens.
One other level that may probably assist you to eradicate stringing in 3D printing is adjusting the motion velocity. If we assume that the motion velocity is ready too sluggish, i.e. that the extruder nozzle wants an excessive amount of time to get from level A to level B, then stringing also can happen. Nonetheless, if we alter the settings in order that the printing course of is quicker, the heated filament has much less time to string as a result of the extruder nozzle strikes quicker. Which motion velocity is finest right here, in fact, relies upon to a sure extent on the 3D printer itself, nevertheless it also needs to be ensured that the motion velocity isn’t too excessive and on the similar time the temperature isn’t set too low, as a result of this is able to result in under-extrusion. One other resolution is that there are literally some slicers that provide the operate that whereas the extruder strikes over areas that aren’t to be printed, the velocity is elevated.
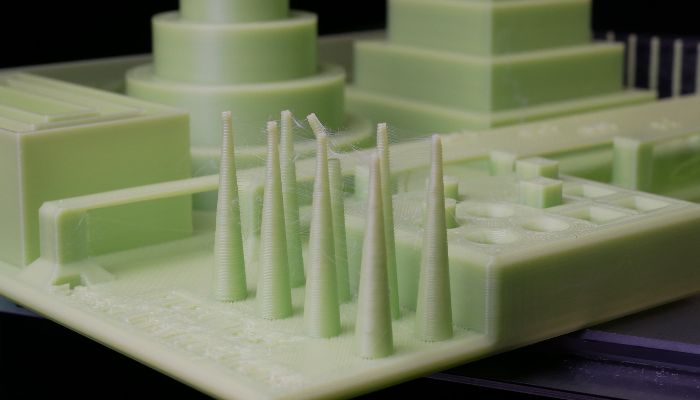
Photograph Credit: Prusa
In all probability the simplest technique to resolve stringing facilities on retraction. Energetic retraction merely implies that when the extruder travels a path on which no strain is utilized, the filament retracts somewhat throughout this time in order that no dripping happens. As soon as the extruder reaches the purpose the place 3D printing is to proceed, the filament is pushed out once more. To take up the instance of the new glue gun once more: Think about that as quickly because the gluing course of is to be interrupted, you pull again the glue stick by hand, thus avoiding the pulling of threads. It’s in all probability advantageous so that you can know that the retraction is normally already activated with slicers.
Additionally, regarding the upkeep of the nozzle and the filament itself, there are some issues that may assist you. On the one hand, it’s best to at all times ensure that the nozzle of your 3D printer is clear. If there are materials residues within the nozzle, there’s a higher threat that items of filament will subsequently be deposited on these residues, which implies that unhindered 3D printing can not happen and threads can kind. The nozzle also needs to be inspected in any case in order that it may be ensured that it isn’t broken. So far as the filament is worried, you will need to level out that it’s dry, as a result of whether it is used for printing in a moist state, the bubbles created because of the moisture can burst through the printing course of and escape from the nozzle unchecked, which might in the end result in stringing.
Now that we’ve got gotten an summary of attainable causes and tips on how to repair them, it’s nonetheless vital to say how one can do away with the skinny filament threads as soon as they’ve been printed. Since – as we’ve got already talked about – there isn’t a automated resolution for eradicating the filaments, sadly you in all probability haven’t any selection however to take away them manually. For this, relying on the complexity of the half, a cautious strategy together with your naked fingers is really helpful. Since stringing entails very skinny threads, they will correspondingly even be simply eliminated with the arms.
Have you ever struggled with stringing? Tell us in a remark beneath or on our LinkedIn, Fb, and Twitter pages! Don’t overlook to enroll in our free weekly E-newsletter right here, the newest 3D printing information straight to your inbox! You too can discover all our movies on our YouTube channel.
*Cowl Photograph Credit: Elliot Saldukaite/ 3Dnatives